Salt Water Barriers
Over the past several decades, excessive pumping has triggered saltwater intrusion, which can threaten that region’s water supplies. As groundwater becomes depleted in the coastal regions, the ocean salt water tends to intrude into the freshwater supplies. This threatens the water for drinking or irrigation as the aquifer becomes contaminated.
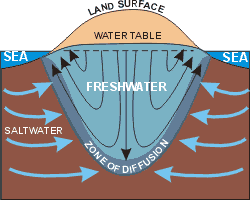
Freshwater, being less dense than seawater, tends to “float” on the saltwater. The Ghyben-Herzberg relationship states that the freshwater zone should extend to a depth below the sea level equal to 40 times the height of the water table above sea level.
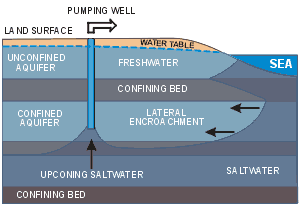
As freshwater heads are lowered through well production, the saltwater migrates towards the point of withdrawal. This movement of water into zones previously containing freshwater is known as saltwater encroachment.
The result is that wells might have to be drilled deeper in the hope that the water available in a lower aquifer has not also been affected. However, where supply wells are drilled too deeply or are pumped at too large a rate, upconing of the salty water may occur.
It is common practice to inject fresh water into the ground to form a “barrier” or “curtain”. This barrier prevents salt water entering the aquifer by providing a hydraulic barrier to sea water intrusion and permitting the groundwater basin to be safely drawn down below sea level. Some of the water that is pumped into this barrier will dissipate into the ocean, while the majority flows back into the groundwater basin thereby augmenting the groundwater supply.
Under these conditions steel pipes are subject to corrosion and can be difficult to manoeuvre. Even stainless steel pipes are subject to corrosion and internal scaling. The result is that the pumps would have to run for longer periods of time to ensure the same quantity of groundwater is being removed from the offending aquifer.
Because of its construction and the sophisticated use of modern materials, Boreline® is not subject to these effects and can be used continually over many years without any form of degradation.